Custard Sauce Production Line
Custard Sauce Production Line
Custard Sauce Production Line
Production Video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AkAcycJx0pI
A custard sauce production line involves a series of automated and semi-automated processes to manufacture custard sauce efficiently, consistently, and hygienically. Below is a detailed breakdown of the typical stages in a custard sauce production line:
1. Ingredient Handling & Preparation
- Milk Reception & Storage
- Raw milk is received, tested for quality, and stored in refrigerated silos.
- Alternative: Reconstituted milk powder + water (for longer shelf life).
- Sugar & Sweetener Handling
- Sugar, corn syrup, or alternative sweeteners are weighed and dissolved.
- Egg & Egg Powder Processing
- Liquid eggs (pasteurized) or egg powder is mixed with water.
- Starch & Stabilizers
- Cornstarch, modified starch, or thickeners (e.g., carrageenan) are pre-mixed to prevent clumping.
- Flavorings & Additives
- Vanilla, caramel, or other flavors, along with preservatives (if needed), are prepared.
2. Mixing & Blending
- Batch or Continuous Mixing
- Ingredients are combined in a high-shear mixer or premix tank under controlled temperatures (to avoid premature thickening).
- Homogenization may be applied for smooth texture.
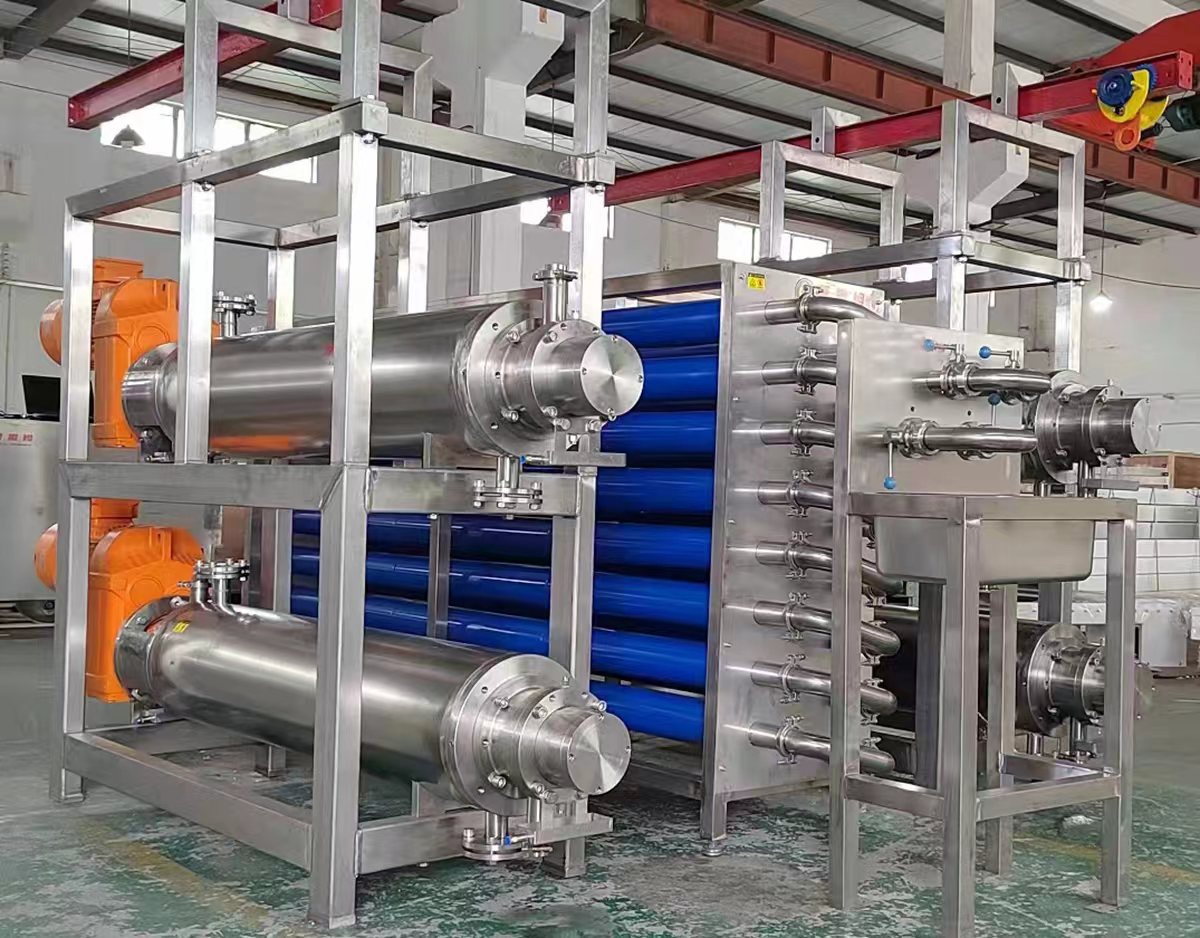
3. Cooking & Pasteurization
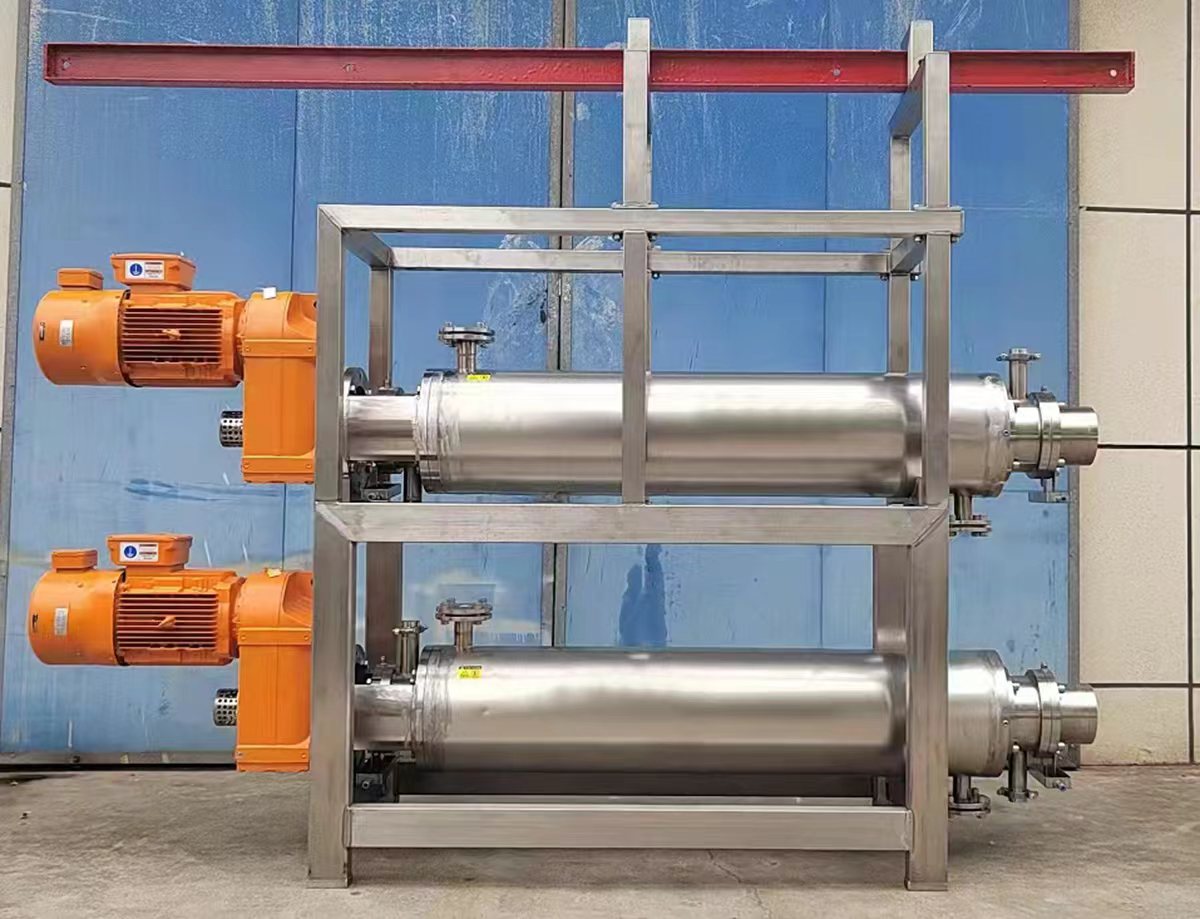
- Continuous Cooking (Scraped Surface Heat Exchanger)
- The mixture is heated to 75–85°C (167–185°F) to activate starch gelatinization and thicken the sauce.
- Pasteurization (HTST or Batch)
- High-Temperature Short-Time (HTST) at 72°C (161°F) for 15-20 sec or batch pasteurization to ensure microbial safety.
- Cooling Phase
- Rapid cooling to 4–10°C (39–50°F) to stop further cooking and maintain texture.
4. Homogenization (Optional)
- High-Pressure Homogenizer
- Used for ultra-smooth texture (prevents graininess).
5. Filling & Packaging
- Automatic Filling Machines
- Pouch filling (for retail) or bulk filling (for foodservice).
- Aseptic filling (for long shelf life) or hot-fill (for ambient storage).
- Packaging Formats:
- Plastic bottles, cartons, pouches, or cans.
- Nitrogen flushing may be used to extend shelf life.
6. Cooling & Storage
- Blast Chilling (if required)
- For refrigerated custard, rapid cooling to 4°C (39°F).
- Cold Storage
- Stored at 4°C (39°F) for fresh custard or ambient for UHT-treated products.
7. Quality Control & Testing
- Viscosity Checks (using viscometers).
- pH Monitoring (target: ~6.0–6.5).
- Microbiological Testing (total plate count, yeast/mold).
- Sensory Evaluation (taste, texture, color).
Key Equipment in Custard Sauce Production Line
- Storage Tanks (for milk, liquid ingredients).
- Weighing & Dosing Systems.
- High-Shear Mixers & Premix Tanks.
- Pasteurizer (HTST or Batch).
- Scraped Surface Heat Exchanger (for cooking).
- Homogenizer (optional).
- Filling Machines (piston, volumetric, or aseptic).
- Cooling Tunnels.
- Packaging Machines (sealing, labeling).
Types of Custard Sauce Produced
- Refrigerated Custard (short shelf life, fresh taste).
- UHT Custard (long shelf life, sterilized).
- Powdered Custard Mix (for reconstitution).
Automation & Efficiency
- PLC Control Systems for precise temperature and mixing control.
- CIP (Clean-in-Place) Systems for hygiene.
Site Commissioning

Write your message here and send it to us